Mumps: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention
Mumps is a contagious viral infection primarily known for causing painful swelling of the salivary glands, located just below and in front of the ears. It is caused by the mumps virus, which belongs to the Paramyxovirus family. Mumps is highly contagious and spreads through respiratory droplets, making close contact with an infected person a common mode of transmission. The virus can also survive on surfaces for several hours, increasing the risk of exposure.

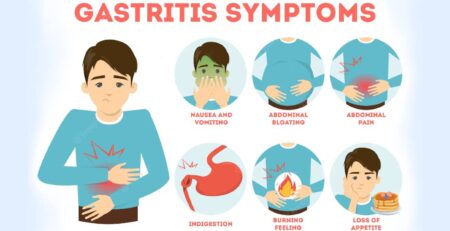
Symptoms: The most recognizable symptom of mumps is the swelling of the salivary glands, leading to a distinctive “chipmunk cheek” appearance. Other common symptoms include fever, headache, muscle aches, fatigue, loss of appetite, and pain while chewing or swallowing. While most cases of mumps are mild, complications can arise, especially in adolescents and adults. These complications can include orchitis (testicular inflammation) in males, which can lead to infertility, as well as inflammation of the ovaries in females. Additionally, mumps can cause viral meningitis, an infection of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord.
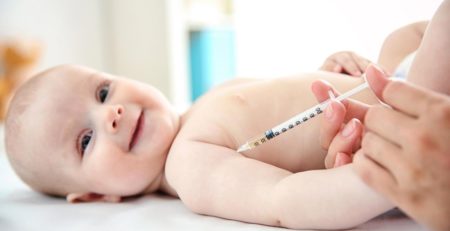
Prevention: The most effective way to prevent mumps is through vaccination. The MMR vaccine, which stands for measles, mumps, and rubella, provides immunity against these three diseases. It is typically administered in two doses, the first around the age of one and the second between the ages of four and six. The vaccine has been remarkably successful in reducing mumps cases since its introduction, but outbreaks can still occur in communities with low vaccination rates.

Treatment: There is no specific antiviral treatment for mumps. Management mainly involves relieving symptoms. Pain relievers, fever reducers, warm or cold compresses to alleviate gland discomfort, and staying hydrated are common recommendations. Infected individuals should also be isolated to prevent further spread of the virus.
In conclusion, mumps is a contagious viral infection that primarily affects the salivary glands, causing characteristic swelling and discomfort. While the introduction of the MMR vaccine has significantly reduced the prevalence of mumps, outbreaks can still occur in under-vaccinated populations. Understanding the symptoms, practicing good hygiene, and ensuring timely vaccination are crucial steps in preventing and managing mumps infections. If symptoms are suspected, seeking medical advice is recommended for appropriate care and guidance.
Dr. Ankit Agarwal (MD Paediatrics, New Born and Child Specialist) is working in this field for last more than 10 years. For more information or for appointment call 90935-90936